Curious about Fertilizer Price in Pakistan? Fertilizer Price in Pakistan fluctuate every day, today Sona Urea Price in Pakistanranges from 4,600/- PKR – 4,800/- PKR and Sona DAP Price in Pakistanranges from 11,900/- PKR – 12,100/- PKR. Fertilizer prices totally depend on its demand and supply.
Fertilizers are vital components of modern agriculture, addressing the ever-pressing need for increased food production to support a growing global population. These essential substances rejuvenate the soil, ensuring that crops receive the requisite nutrients for robust growth. Among the diverse array of fertilizers available, DAP (Diammonium Phosphate) and Urea stand out as two of the most prevalent. In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the realm of fertilizers, exploring their definition, various types, and their profound impact on agriculture and the environment. Fertilizer price in Pakistan not stable, it depend on dollar price and international market. Fertilizer Price in Pakistan are following.
Fertilizer Price in Pakistan
| Fertilizer Name | Local Market Price | Local Market Trend |
| Sona DAP | Rs. 11,800 PKR to Rs. 11,950 PKR | |
| Engro DAP | Rs. 11,800 PKR to Rs. 11,950 PKR | |
| Sarsabz DAP | Rs. 11,700 PKR to Rs. 11,850 PKR | |
| FFC DAP | Rs. 11,700 PKR to Rs. 11,900 PKR | |
| Sona Urea | Rs. 4,550 PKR to Rs. 4,600 PKR | |
| Engro Urea | Rs. 4,550 PKR to Rs. 4,600 PKR | |
| Sarsabz NP | Rs. 7,300 PKR to Rs. 7,400 PKR | |
| Zarkhez Plus | Rs. 9,000 PKR to Rs. 9,100 PKR | |
| Sarsabz Can Gawara | Rs. 4,550 PKR to Rs. 4,600 PKR | |
| Pak Arab Gawara | Rs. 4,400 PKR to Rs. 4,500 PKR | |
| Zabardast Urea | Rs. 5,000 PKR to Rs. 5,300 PKR |
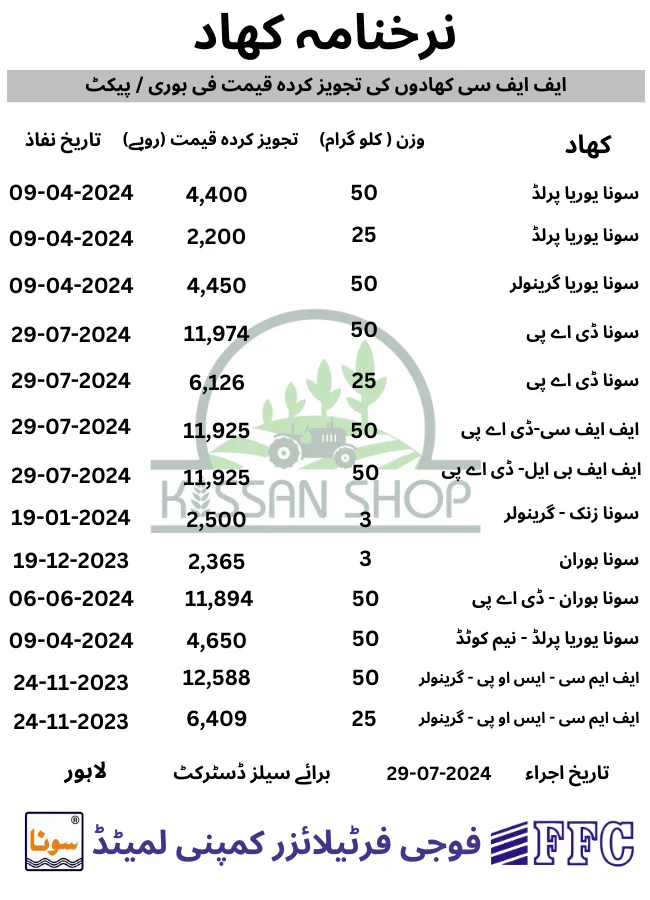
Fertilizer Price in Pakistan are fluctuate in these days. Everyday Fertilizer Price are increase in these days. Fertilizer control price from government of Pakistan mentioned in above. But in local market fertilizer not sell out on control price. Such as Sona DAP fertilizer price in Pakistan from Government is 11,974/- PKR but in local Market Sona DAP Price in Pakistan today is 11,900/- PKR. Engro DAP Price in Pakistan today is 11,850/- PKRin local market. Engro Fertilizer Price list is below:
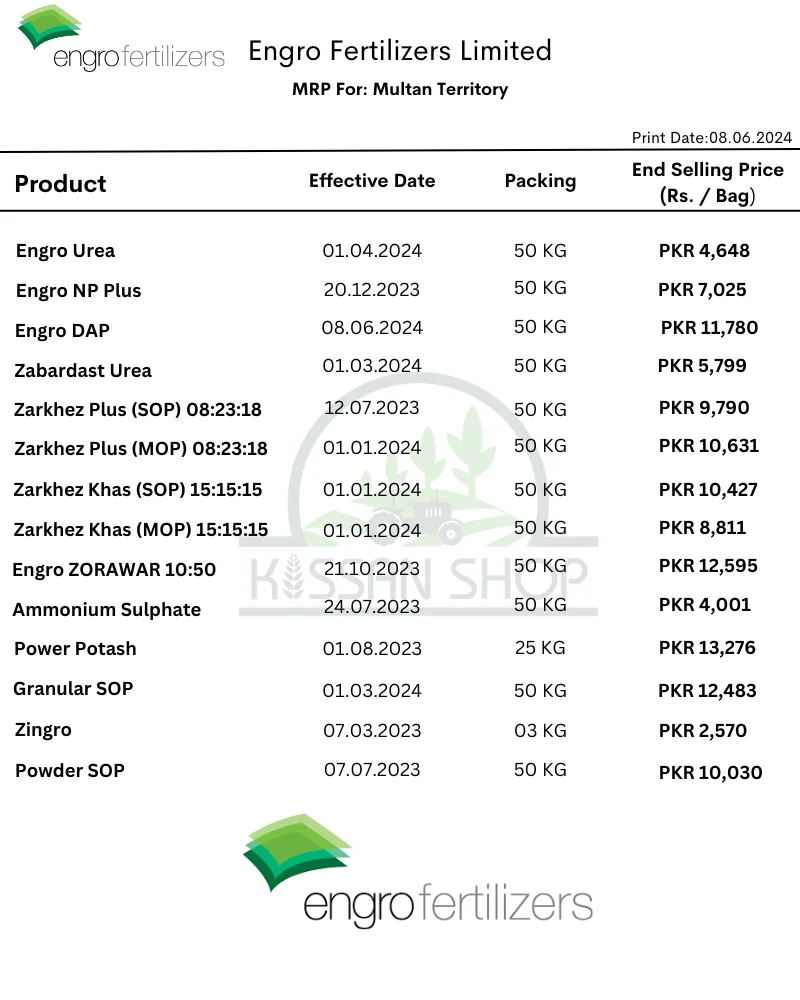
Further, Sona Urea Price in Pakistan increased from Government is 4,650/- PKR and in local Market Sona Urea Price in Pakistan today is 4,800/- PKR. In following table current fertilizer price in Pakistan mentioned. In local market fertilizers are selling on this price. Fatima Fertilizer Price List is below:

Table of Contents
Fertilizer Companies in Pakistan
What are Fertilizers? Types, Uses and Advantage
Chapter 1: Fertilizers Unveiled
1.1 Decoding Fertilizers
1.2 The Significance of Macronutrients
1.2.1 Nitrogen (N)
1.2.2 Phosphorus (P)
1.2.3 Potassium (K)
Chapter 2: Inorganic Fertilizers
2.1 Diammonium Phosphate (DAP)
2.1.1 Composition and Characteristics
2.1.2 Application and Benefits
2.1.3 Environmental Considerations
2.2 Urea Fertilizer
2.2.1 Composition and Characteristics
2.2.2 Application and Advantages
2.2.3 Environmental Impact
Chapter 3: Organic Fertilizers
3.1 Compost
3.1.1 Composition and Attributes
3.1.2 Application and Merits
3.2 Manure
3.2.1 Composition and Traits
3.2.2 Application and Benefits
Chapter 4: Sustainable Fertilizer Practices
4.1 Precision Agriculture
4.2 Nutrient Management Plans
4.3 Organic Farming
Chapter 5: Environmental Impact and Sustainability
5.1 Nutrient Runoff
5.2 Eutrophication
5.3 Sustainable Agriculture
Chapter 6: Future Trends in Fertilizer Use
6.1 Controlled-Release Fertilizers
6.2 Biodegradable Fertilizers
6.3 Nutrient Recovery
Conclusion
Benefits of Using Fertilizers in Agriculture
Increased Crop Yields:
Nutrient Balance:
Enhanced Plant Growth:
Quick Nutrient Availability:
Precision Farming
Improved Soil Fertility
Crop Variety Suitability
Weather Resilience
Reduced Land Expansion:
Global Food Security
Economic Benefits:
Innovation and Sustainability
Fertilizers used in land (soil) for several important reasons:
Nutrient Deficiency
Increased Crop Yields:
Balanced Nutrition
Quick Nutrient Availability
Precision Farming
Improved Soil Fertility
Weather Resilience:
Reduced Land Expansion
Global Food Security
Economic Benefits
Conclusion
Fertilizer Companies in Pakistan
As of my last knowledge update in July 2024, Pakistan has several fertilizer companies that play a significant role in the country’s agriculture sector. Fertilizer Price in Pakistan are different in all companies. Here are some of the prominent fertilizer companies operating in Pakistan are follows:
- Engro Fertilizers Limited: One of the largest fertilizer companies in Pakistan, Engro Fertilizers produces a range of fertilizers, including urea and phosphate-based fertilizers. They are known for their brand “Engro.”
- Fauji Fertilizer Company Limited (FFC): FFC is another major player in Pakistan’s fertilizer industry, producing various types of fertilizers. Their popular brands include “Sona Urea” and “Sona DAP.”
- Fatima Fertilizer Company Limited: Fatima Fertilizers is involved in the manufacturing and marketing of a wide range of fertilizers, including urea and phosphate fertilizers.
- Dawood Hercules Corporation Limited: This company is involved in various industries, including fertilizers. They operate under the brand name “Brite.”
- Fauji Fertilizer Bin Qasim Limited (FFBL): FFBL is a subsidiary of Fauji Fertilizer Company Limited, and it specializes in the production of di-ammonium phosphate (DAP) fertilizers.
- Pakarab Fertilizers Limited: Pakarab Fertilizers is known for producing calcium ammonium nitrate (CAN Guwara) and other fertilizer products.
- Engro Powergen Qadirpur Limited (EPQL): A subsidiary of Engro Corporation, EPQL is involved in power generation and also produces a limited quantity of fertilizer.
Please note that the fertilizer industry is subject to changes, mergers, and acquisitions, and the landscape may have evolved since my last update. For the most current information on fertilizer companies in Pakistan, it’s advisable to consult authoritative sources, industry reports, or the official websites of these companies. In local Market there are three most famous companies, first Fauji Fertilizer, second one is Engro Fertilizer and third is Fatima Fertilizer. So, fertilizer price in Pakistan of these companies is high as compare to others.
What are Fertilizers? Types, Uses and Advantage
Fertilizers play a pivotal role in modern agriculture, ensuring that crops receive the essential nutrients needed for optimal growth and productivity. In Pakistan, the use of fertilizers has significantly contributed to the agricultural sector, enhancing crop yields and supporting the livelihood of millions of farmers. This article delves into the world of fertilizers, exploring their types, uses, advantages, and the various fertilizer companies operating in Pakistan. Additionally, we will examine sustainable fertilizer practices, the environmental impact of fertilizer use, and future trends in the industry.
Chapter 1: Fertilizers Unveiled
1.1 Decoding Fertilizers
Fertilizers are substances that provide essential nutrients to plants, promoting their growth and enhancing their productivity. These nutrients are typically divided into macronutrients and micronutrients, with macronutrients being required in larger quantities. The primary macronutrients are nitrogen (N), phosphorus (P), and potassium (K), often referred to as NPK.
1.2 The Significance of Macronutrients
Macronutrients are crucial for plant development and play specific roles in various physiological processes.
1.2.1 Nitrogen (N)
Nitrogen is a vital component of chlorophyll, the compound that plants use in photosynthesis to convert sunlight into energy. It is also a key element in amino acids, the building blocks of proteins, and is essential for the growth of leaves and stems.
1.2.2 Phosphorus (P)
Phosphorus is essential for energy transfer within plants, playing a crucial role in the formation of ATP (adenosine triphosphate), which plants use to store and transfer energy. It also contributes to the development of roots, flowers, and seeds.
1.2.3 Potassium (K)
Potassium helps regulate various plant processes, including water uptake, enzyme activation, and photosynthesis. It is essential for the overall health and resilience of plants, improving their resistance to diseases and environmental stresses.
Chapter 2: Inorganic Fertilizers
Inorganic fertilizers are synthetic or mined products that provide specific nutrients to plants. They are widely used due to their high nutrient content and immediate availability.
2.1 Diammonium Phosphate (DAP)
2.1.1 Composition and Characteristics
Diammonium phosphate (DAP) is a widely used phosphorus fertilizer that also provides a significant amount of nitrogen. Its chemical formula is (NH4)2HPO4, and it typically contains 18% nitrogen and 46% phosphorus pentoxide (P2O5).
2.1.2 Application and Benefits
DAP is highly soluble in water, making it readily available to plants. It is commonly applied at planting time to support root development and early plant growth. The presence of both nitrogen and phosphorus makes it a valuable fertilizer for a wide range of crops.
2.1.3 Environmental Considerations
While DAP is effective in promoting plant growth, its excessive use can lead to environmental issues such as nutrient runoff and water pollution. Sustainable application practices are essential to minimize these impacts.
2.2 Urea Fertilizer
2.2.1 Composition and Characteristics
Urea is one of the most widely used nitrogen fertilizers. It contains 46% nitrogen, making it one of the most concentrated nitrogen sources available. Urea is a white crystalline solid that is highly soluble in water.
2.2.2 Application and Advantages
Urea is applied to the soil and can be used in various forms, including granules, pellets, or as a foliar spray. It provides a quick release of nitrogen, promoting rapid plant growth and green foliage. Urea is cost-effective and suitable for a wide range of crops.
2.2.3 Environmental Impact
Improper application of urea can lead to nitrogen losses through volatilization and leaching, contributing to environmental pollution. Efficient application methods and timing are crucial to minimize these losses.
Chapter 3: Organic Fertilizers
Organic fertilizers are derived from natural sources and contribute to soil health by improving its structure and nutrient content.
3.1 Compost
3.1.1 Composition and Attributes
Compost is made from decomposed organic matter, including plant residues, kitchen waste, and manure. It is rich in organic matter, nutrients, and beneficial microorganisms that enhance soil fertility.
3.1.2 Application and Merits
Compost is applied to the soil to improve its structure, water-holding capacity, and nutrient content. It releases nutrients slowly, providing a steady supply to plants over time. Compost also enhances soil microbial activity and supports sustainable farming practices.
3.2 Manure
3.2.1 Composition and Traits
Manure is an organic fertilizer derived from animal waste, including cattle, poultry, and sheep manure. It is rich in nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium, as well as organic matter that improves soil structure.
3.2.2 Application and Benefits
Manure is applied to the soil to enhance its fertility and structure. It provides a slow release of nutrients and improves soil moisture retention. Manure also supports soil microbial activity and contributes to sustainable agriculture.
Chapter 4: Sustainable Fertilizer Practices
4.1 Precision Agriculture
Precision agriculture involves the use of technology to apply fertilizers and other inputs precisely where and when they are needed. This approach minimizes waste, reduces environmental impact, and enhances crop productivity.
4.2 Nutrient Management Plans
Nutrient management plans involve the careful planning and application of fertilizers to meet crop needs while minimizing nutrient losses. These plans take into account soil tests, crop requirements, and environmental considerations.
4.3 Organic Farming
Organic farming relies on natural inputs and practices to maintain soil fertility and promote sustainable agriculture. Organic fertilizers, crop rotations, and biological pest control are key components of organic farming systems.
Chapter 5: Environmental Impact and Sustainability
5.1 Nutrient Runoff
Nutrient runoff occurs when excess fertilizers are washed away from fields into water bodies, leading to water pollution and eutrophication. Effective nutrient management practices are essential to minimize nutrient runoff.
5.2 Eutrophication
Eutrophication is the process by which water bodies become enriched with nutrients, leading to excessive growth of algae and other aquatic plants. This can result in oxygen depletion and harm aquatic life. Reducing fertilizer runoff is crucial to prevent eutrophication.
5.3 Sustainable Agriculture
Sustainable agriculture aims to meet the needs of the present without compromising the ability of future generations to meet their own needs. It involves the use of environmentally friendly practices, efficient resource use, and the conservation of biodiversity.
Chapter 6: Future Trends in Fertilizer Use
6.1 Controlled-Release Fertilizers
Controlled-release fertilizers are designed to release nutrients gradually over time, matching the nutrient uptake pattern of crops. This reduces nutrient losses and enhances nutrient use efficiency.
6.2 Biodegradable Fertilizers
Biodegradable fertilizers are made from materials that break down naturally in the environment. They provide nutrients to plants while reducing environmental impact and minimizing waste.
6.3 Nutrient Recovery
Nutrient recovery involves the capture and reuse of nutrients from waste streams, such as animal manure or wastewater. This approach reduces nutrient losses and promotes a circular economy in agriculture.
Conclusion
The use of fertilizers is essential for modern agriculture, contributing to increased crop yields, improved soil fertility, and enhanced food security. Understanding the types, uses, and advantages of fertilizers, along with sustainable practices, is crucial for maximizing their benefits while minimizing environmental impact. The future of fertilizer use lies in the adoption of innovative technologies and sustainable practices that promote efficient nutrient management and environmental stewardship.
Benefits of Using Fertilizers in Agriculture
Increased Crop Yields
Fertilizers provide essential nutrients that boost crop growth and increase yields, supporting food security and farmer livelihoods.
Nutrient Balance
Fertilizers ensure a balanced supply of nutrients, preventing deficiencies and promoting healthy plant growth.
Enhanced Plant Growth
Fertilizers support vigorous plant growth, improving overall crop health and productivity.
Quick Nutrient Availability
Inorganic fertilizers provide a quick release of nutrients, meeting the immediate needs of growing plants.
Precision Farming
Precision farming techniques optimize fertilizer application, reducing waste and improving efficiency.
Improved Soil Fertility
Organic fertilizers enhance soil structure and fertility, supporting sustainable agriculture.
Crop Variety Suitability
Different fertilizers can be tailored to meet the specific nutrient needs of various crops, enhancing their growth and yield.
Weather Resilience
Fertilizers help crops withstand adverse weather conditions, improving resilience and stability.
Reduced Land Expansion
By increasing yields on existing farmland, fertilizers reduce the need for agricultural expansion into natural ecosystems.
Global Food Security
Fertilizers play a crucial role in ensuring global food security by increasing agricultural productivity.
Economic Benefits
Increased crop yields and productivity lead to higher incomes for farmers, contributing to rural development and economic growth.
Innovation and Sustainability
Advances in fertilizer technology and sustainable practices support innovation and long-term agricultural sustainability.
Fertilizers Used in Land (Soil) for Several Important Reasons
Nutrient Deficiency
Fertilizers address nutrient deficiencies in soil, providing the essential elements needed for plant growth.
Increased Crop Yields
Fertilizers boost crop yields by supplying nutrients that enhance plant growth and productivity.
Balanced Nutrition
Fertilizers ensure balanced nutrition for plants, preventing deficiencies and promoting healthy development.
Quick Nutrient Availability
Inorganic fertilizers provide rapid nutrient availability, meeting the immediate needs of crops.
Precision Farming
Precision farming techniques optimize fertilizer application, reducing waste and improving efficiency.
Improved Soil Fertility
Organic fertilizers enhance soil structure and fertility, supporting sustainable agriculture.
Weather Resilience
Fertilizers help crops withstand adverse weather conditions, improving resilience and stability.
Reduced Land Expansion
By increasing yields on existing farmland, fertilizers reduce the need for agricultural expansion into natural ecosystems.
Global Food Security
Fertilizers play a crucial role in ensuring global food security by increasing agricultural productivity.
Economic Benefits
Increased crop yields and productivity lead to higher incomes for farmers, contributing to rural development and economic growth.
Conclusion
The use of fertilizers is indispensable for modern agriculture, enhancing crop yields, improving soil fertility, and ensuring global food security. By understanding the different types of fertilizers, their uses, and advantages, farmers can optimize their agricultural practices for maximum productivity and sustainability. The future of fertilizer use lies in the adoption of innovative technologies and sustainable practices that promote efficient nutrient management and environmental stewardship.

